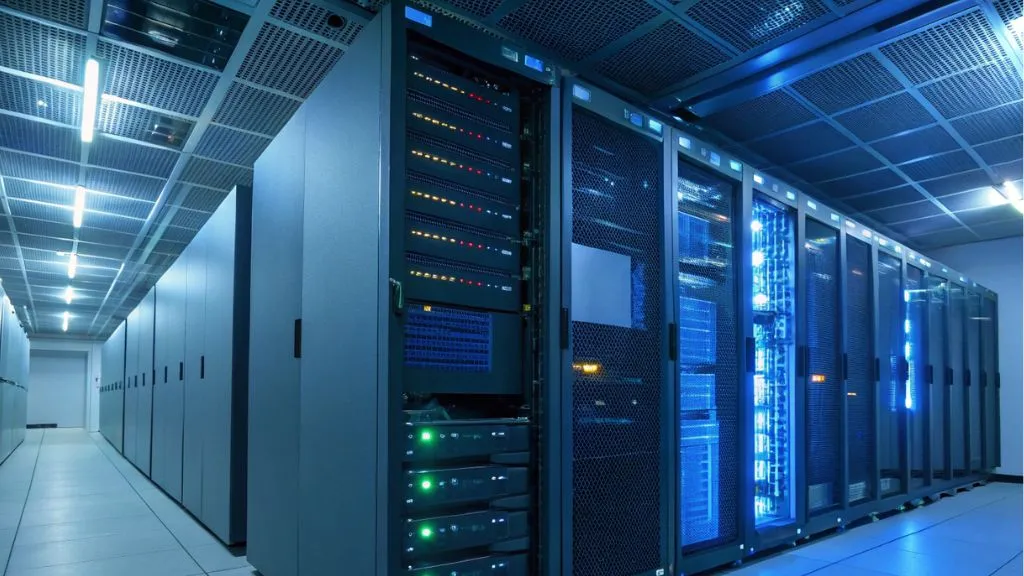

Cloud technologies (or “the cloud”) have become one of the main tools for business transformation in the context of digitalization. Thanks to such technologies, companies around the world can reduce costs and increase the flexibility and adaptability of their operations. The cloud allows you to access the necessary resources and programs via the Internet without the need to own physical equipment, and all operations are carried out through a remote infrastructure. In this article, we will take a detailed look at what cloud technologies are, how they work, their advantages and disadvantages for business, and share our predictions for the future development of the cloud.
In today’s world, companies no longer want to invest huge sums in deploying and maintaining their own servers and infrastructure. Here are the main reasons why businesses are actively moving to cloud technologies:
Cloud technologies are a model for providing IT resources via the Internet. This means that companies can store their data on remote servers, run applications, and perform other operations without the need to own expensive physical resources. What is referred to as cloud technology depends on the context, but it usually refers to the virtualization of resources provided over the Internet, allowing businesses to store data, run applications, and use various services without the need for local infrastructure.
The idea behind cloud technologies is to move infrastructure, software, and data storage to servers owned by service providers and access them via the Internet. This saves money on physical devices and allows you to scale resources, add new features as needed, and pay only for actual usage.
Imagine you are working on a document in Google Docs. The document itself is stored in the cloud, and you can access it from any device, whether it’s a phone, tablet, or computer, with a simple login. There is no need to store it on your computer’s hard drive or purchase servers to store large files.
Cloud technologies are a powerful tool that allows companies to store, process, and transfer data without the need to deploy physical infrastructure. All these operations are carried out via the Internet, and most processes are hidden behind a simple interface that users can access from anywhere in the world. What devices can cloud technologies be used on? They are available on any device with an Internet connection, such as computers, smartphones, tablets, and even specialized IoT devices, allowing access to data and applications from anywhere in the world. Let’s take a look at how cloud technologies work and what components make them possible.
Data centers are key components of cloud technologies. These are physical or virtual facilities containing powerful servers that store and process data. They are equipped with large memory arrays, disks, and processors capable of handling a huge number of requests simultaneously.
Data centers have several key advantages:
Data centers operate 24/7 and provide reliable data storage, request processing, and services available to users around the world.
Virtualization is a technology that allows you to create virtual servers using physical servers. This means that instead of spending separate physical resources (which will be underutilized) on each server, servers can be divided into several virtual servers that share common resources.
The main characteristics of virtual servers:
Virtualization also allows you to create specialized servers for specific tasks, such as running databases, web applications, or analyzing big data.
The user interface (UI) is the main way to interact with cloud services. Although cloud technologies themselves take place in the backend, users have access to all resources through an intuitive web interface or mobile applications. These can be control panels or specialized programs that provide access to all cloud functions.
The main functions of the user interface:
Cloud user interfaces typically have a high level of security, including two-factor authentication and data encryption to protect access.
The whole process takes place via a stable Internet connection, which allows you to access all resources and data at any time and from anywhere in the world. The connection to the cloud is made via a secure connection that ensures the speed and security of data transmission. The underlying infrastructure, including servers and networks, is located in data centers, which allows you to work with large amounts of data without local restrictions.
Thanks to the distributed architecture, data and applications can be accessed simultaneously by many users around the world, while providing reliable protection and backup in case of failures.
In such a system, all data exchange is carried out through user interfaces that allow you to quickly set up access, process data, and perform other important operations. The user does not need to understand the technical details, as all these processes are automated.
Thus, the cloud functions as an integrated system where all parts – data centers, servers, interfaces, and other components – work synchronously, providing fast and secure access to resources via the Internet.
There are various cloud computing models, each with its own advantages, disadvantages, and specific use cases. Choosing the right model depends on your specific business needs, company size, security, access to resources, and budget. The choice of cloud model can affect the company’s efficiency, ability to scale resources and maintain operational stability.
A public cloud is a cloud service model where infrastructure and resources, such as servers, storage, and networks, are provided by an external provider over the Internet and are available for use without any restrictions by other users. This means that the physical infrastructure and server capacity are not directly owned by the users, but are managed by a third party provider who is responsible for its maintenance, upgrades, backups, and security.
Since public cloud resources are shared with other users, businesses can benefit from significant cost savings. For small and medium-sized companies that do not have large infrastructure budgets, the public cloud is an ideal solution because they pay only for the actual use of resources, not for physical servers or equipment. This reduces the initial investment and eliminates the need for ongoing support and maintenance costs.
The public cloud provides high scalability, allowing businesses to instantly increase or decrease their resources depending on their needs. When demand for products or services increases, companies can increase capacity without waiting for physical hardware to be delivered and installed. Once the need for resources decreases, they can be quickly scaled down or shut down, which also contributes to savings.
The public cloud provides instant access to advanced technologies and tools, such as data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, developer tools, and other platforms that may not be available to smaller companies if they had to invest in physical infrastructure. Companies using the public cloud can easily integrate new technologies and tools into their operations without having to upgrade or modernize their own servers.
Public clouds usually have a high level of reliability due to the fact that service providers have multiple data centers in different geographical locations to ensure continuous operation and backup data recovery. This means that companies can use the cloud services even in the event of an accident or failure of one of the data centers.
Public clouds typically offer intuitive user interfaces that allow you to get up and running quickly without the need for specialized knowledge. This means that companies can focus on their core business rather than on server or infrastructure maintenance. Cloud service providers also automatically handle software updates, bug fixes, and system security.
Since public clouds do not require significant financial investments to launch, they become attractive to startups, small and medium-sized businesses. Businesses can get access to advanced cloud technologies and scalable resources without having to spend significant funds on their own infrastructure. This makes it easier for new players to enter the market, so they can focus on business development rather than server maintenance.
Examples of using the public cloud:
In summary, the public cloud is an affordable, efficient, and scalable solution for businesses that want to focus on developing their product or service rather than managing physical resources or server infrastructure. It allows you to innovate quickly, reduce costs, and achieve high reliability and security at minimal cost.
A private cloud is a cloud intended for use by a single organization, where all infrastructure and resources belong to only one user or company. Unlike a public cloud, where resources are shared among multiple users, a private cloud provides complete control over data, security, access, and configuration. This gives companies the ability to manage all aspects of the cloud infrastructure according to their specific requirements. Private clouds are typically used by large corporations, banks, government agencies, and other organizations that have high security requirements and complete control over their data.
A private cloud gives a company full control over all resources, including servers, networks, and storage. This allows organizations to optimize their infrastructure setup for their specific needs. For example, companies can choose the type and configuration of servers, data storage methods, and set specialized security policies.
A private cloud allows organizations to provide a high level of security for their data. Since the cloud resources are used by only one organization, stricter security standards can be implemented and stricter access restrictions can be set. For organizations that work with sensitive information (banks, medical institutions, government organizations), this is an important advantage, as it reduces the risk of data leakage or unauthorized access.
In a private cloud, resources are completely isolated from other users, providing guaranteed performance and stability. It also allows businesses to optimize resources for specific tasks, such as processing large amounts of data or high-performance computing. Each server or virtual machine can be configured to perform specific tasks based on performance requirements.
In a private cloud, companies can customize the system to solve very specific problems. For example, organizations can implement customized applications that meet their specifications. This is especially important for large companies with complex requirements, such as large manufacturing plants or medical institutions that need specific data processing software.
The private cloud makes it possible to localize data in specific geographical areas or countries, which meets the requirements of local laws or regulations, such as GDPR in the European Union or HIPAA in the United States for healthcare. This allows companies to comply with all legal regulations regarding data storage and processing.
Examples of using a private cloud:
Disadvantages of a private cloud:
Private cloud is an ideal solution for organizations that require higher security, complete control over data, and privacy, but it also comes with higher costs and technical requirements to maintain and scale the infrastructure.
Hybrid cloud is a cloud technology model that combines elements of both public and private clouds. This combination allows organizations to leverage the best features of both approaches, providing an optimal balance between security and scalability. The main goal of a hybrid cloud is to provide maximum flexibility and the ability to manage resources and data, depending on their sensitivity and importance to the business.
In a hybrid cloud, a company can store its most critical data, such as financial information, personal customer data, or strategic documents, in a private cloud where it is fully protected and under the company’s control. At the same time, less important data that does not require this level of protection can be stored in the public cloud, which reduces infrastructure costs and takes advantage of its scalability.
Hybrid cloud allows organizations to adapt to changes in needs and workload. For example, during peak periods when demand for services increases, companies can increase resources using the public cloud without worrying about the limitations of private infrastructure. After the load drops, resources in the public cloud can be reduced to a minimum, which provides savings.
Hybrid cloud allows you to optimize costs by storing critical data in a private cloud where a high level of security is ensured, while less important data can be stored in the public cloud where it is accessible, scalable, and less expensive to maintain. This enables organizations to balance infrastructure costs and maximize the benefits of both cloud models.
With the ability to store data in both private and public clouds, hybrid solutions allow companies to ensure high availability of their services and business continuity. If one part of the system in the private cloud fails, the business can quickly switch the load to another part of the cloud or use backup resources in the public cloud.
Examples of hybrid cloud usage:
Disadvantages of the hybrid cloud:
Hybrid cloud is a highly flexible and effective solution for companies that want to combine the benefits of private and public clouds while ensuring high security for critical data and optimizing infrastructure costs. It is ideal for organizations that have mixed data requirements and want to maximize the efficiency of their operations in a cloud environment.
Multi-cloud is a strategy where companies use multiple cloud providers simultaneously, combining different services from different vendors to perform different tasks. This allows organizations to take advantage of each provider by choosing the best tools for their specific business needs. Instead of being dependent on a single cloud provider, companies can combine public and private clouds, as well as different services from separate providers, which allows for greater flexibility and security.
One of the main reasons for using multi-cloud is to reduce dependence on a single provider. Choosing multiple providers reduces the risk that a company will find itself in a difficult situation due to technical or financial problems with one provider. In the event of a service failure or security issues in one cloud, the company can quickly switch the load to another cloud, minimizing business risks.
By using multiple providers, companies can optimize the cost of cloud services. For example, one provider might be more cost-effective for data storage, while another might be more cost-effective for big data or machine learning. This allows you to choose the most cost-effective and efficient services for specific tasks, reducing overall infrastructure costs.
Multicloud allows you to distribute data and applications across multiple cloud environments, which provides higher availability and reliability of systems. If one cloud becomes unavailable due to technical issues or outages, other providers can take over, allowing services and applications to continue to operate without interruption.
By using multiple clouds, companies gain more flexibility in choosing tools and technologies. They can quickly adapt their growth and scale strategies by adding or changing services based on business needs. For example, if one cloud can’t handle an increased workload, the company can distribute that workload across several other providers.
Each cloud provider has its own set of tools that can be particularly useful for different business needs. With a multi-cloud strategy, companies can combine the most advanced and innovative services from different providers, allowing them to use the best technology for each individual task.
Examples of multicloud usage:
Disadvantages of multicloud:
Multi-cloud is a powerful tool for large companies that need flexibility, scalability, and reliability in managing cloud resources. Using multiple providers at the same time allows you to reduce risks, avoid dependence on a single vendor, and optimize costs while ensuring a high level of security and availability. However, to use multi-clouds effectively, it is important to consider possible management and integration difficulties, as well as the need for qualified specialists to set up and maintain such systems.
Community Cloud is a cloud model in which the infrastructure and resources of the cloud are shared by multiple organizations that have common interests, needs, or regulatory requirements. This can be a group of businesses in the same industry or organizations operating in the same region, such as hospitals, universities, or government agencies. A shared cloud allows for the pooling of resources and standards to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and provide a higher level of security for all participants.
A public cloud allows organizations to share infrastructure, maintenance, and upgrade costs among multiple participants. This reduces costs for each organization while maintaining a high level of security and efficiency.
Organizations using the public cloud can combine their resources, data, and infrastructure, standardizing processes to improve collaboration and simplify integrations. This allows them to achieve better results and reduce unnecessary duplication of resources.
A public cloud provides a high level of security because access to resources is limited to organizations that belong to the same group or community. This allows companies to comply with specific security regulations and standards that may be important for the industry in which they operate.
A shared cloud allows organizations with similar needs to tailor infrastructure and services to their requirements while still maintaining the benefits of resource sharing.
Examples of using a shared cloud:
Disadvantages of a shared cloud:
The public cloud is an ideal solution for organizations with similar needs and requirements, such as healthcare facilities, universities, or government agencies. It reduces costs, pools resources, and provides a high level of security and control, but requires proper organization and management to avoid potential privacy and flexibility issues.
Cloud technologies offer three main service models that differ in the level of resources and control provided.
Example: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure.
Example: Google App Engine, Heroku.
Example: Google Workspace, Salesforce, Dropbox.
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS provide different levels of cloud services: from infrastructure to ready-made applications. The choice depends on your business needs and the level of control you want.
One of the key issues for businesses is to understand what the main benefits of using cloud technologies are, as they can significantly increase efficiency, reduce costs, and provide flexibility in resource management. Cloud technologies offer businesses many opportunities to optimize operations, reduce costs, and increase efficiency. They allow companies to be more flexible, scalable and competitive, which is especially important in today’s rapidly changing business environment. With cloud-based solutions, businesses can focus on developing their products and services rather than on technical issues such as infrastructure management or data security. In this section, we’ll look at the key business benefits of cloud computing that make it such a popular and important part of digital transformation.
Cloud computing allows businesses to pay only for the resources they actually use, which significantly reduces infrastructure costs. Companies no longer need to invest heavily in physical servers, hardware, or software, as they can rent only what they need at a given time. This is especially beneficial for small and medium-sized enterprises, which can save significant money on maintenance and technical support.
One of the main advantages of cloud computing is its scalability. Businesses can quickly change the amount of computing resources, data storage, or network capacity depending on their current needs. This is especially important for seasonal businesses or those that operate under variable demand, when the load can increase or decrease dramatically. For example, an online store can quickly increase capacity to handle a large number of transactions during sales or holiday periods.
Cloud technologies provide remote access to data and applications, allowing employees to work from anywhere in the world. This is especially important for companies with international teams or businesses that support flexible working conditions. This allows employees to work anytime and from anywhere, which increases efficiency and allows you to attract talent from different regions without being tied to a physical office.
Cloud providers provide a high level of reliability and security through multi-level data protection systems, backup and automatic disaster recovery. The data is stored on reliable and stable servers distributed across different regions, which minimizes the risk of data loss or unforeseen business interruptions. Cloud platforms provide ongoing security support, data updates, and encryption, allowing companies to be confident in the protection of their sensitive data.
Cloud technologies provide access to innovative tools such as artificial intelligence (AI), Big Data, and process automation, which allows businesses to process data more efficiently and make more informed decisions. The cloud allows you to integrate powerful analytical tools, create machine learning systems to predict trends, and automate routine business processes, which reduces the cost of operational tasks and increases the company’s productivity.
While cloud computing offers numerous business benefits, there are also certain cloud computing disadvantages that are important to consider when choosing this model for your company.
Cloud computing offers tremendous business benefits, but it also has its drawbacks. It’s important to carefully assess the potential risks and benefits before moving to cloud services. Each business must consider the specifics of its operations and the level of control, security, and scalability required to operate effectively.
Cloud computing is a versatile tool that can be useful for companies of all sizes and industries. They are suitable for small, medium, and large businesses, but the greatest benefit from cloud solutions comes from those businesses that have specific needs for speed of scale, flexibility, and innovative technologies.
Cloud solutions are ideal for IT companies that develop software, web services, or mobile applications. Thanks to the scalability and flexibility of cloud technologies, these companies can easily process large amounts of data, test new products, and quickly scale their infrastructure as needed. In addition, the cloud provides access to powerful analytical tools that help optimize development processes and increase efficiency.
Startups often have limited budgets and need solutions that minimize initial infrastructure costs. Cloud technologies enable startups to store data, run applications, and use software tools without having to invest in expensive servers or specialized hardware. Thanks to the pay-per-use model, startups can increase or decrease their resources depending on business needs, which avoids spending on unnecessary infrastructure elements.
Online retailers and e-commerce businesses benefit greatly from cloud-based solutions. Cloud platforms allow you to quickly increase resources to process a large number of transactions, store customer and product data, and integrate various services (such as payment systems or delivery services) without the need to invest in infrastructure. In addition, the cloud ensures high availability and continuous operation of websites and online platforms, which is critical for maintaining the operation of online stores.
For large companies, cloud technologies allow them to combine data from different branches and regions, centrally manage infrastructure, and provide access to data and applications for employees around the world. The cloud allows you to efficiently scale resources depending on business growth and minimize the cost of supporting and maintaining servers.
Small and medium-sized businesses can also benefit from cloud computing due to its affordability and ease of use. The cloud allows these companies to reduce infrastructure costs, store data, and use accounting, project management, and communications applications without having to invest heavily in physical servers and hardware. In addition, small businesses can use powerful tools for marketing, data analysis, and process automation that were previously available only to large corporations.
For companies that operate in several countries or have numerous offices, cloud-based solutions enable centralized resource management, storage, and data sharing. Employees from different locations can access shared resources in real time, which simplifies internal communication and improves productivity.
Cloud computing is suitable for any business that wants to be more flexible, reduce infrastructure costs, and be able to quickly adapt to changes. They are most beneficial to IT companies, startups, online retailers, and large corporations, but they can also be extremely useful for small and medium-sized businesses due to their accessibility, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness.
Cloud computing continues to evolve, with new innovative approaches emerging every year that are changing the way we process data, integrate new technologies, and reduce our environmental footprint. Here are some key trends that will shape the future of cloud solutions:
Serverless computing is a cloud service model where developers can run code without having to manage servers or infrastructure. In this model, computing resources are automatically scaled as needed, and companies pay only for the actual time the program is running, not for the amount of resources.
Benefits:
Example: AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions.
Edge computing is a technology that allows data to be processed closer to the source of its generation, for example, on end-user devices or in local nodes, rather than in centralized data centers. This reduces latency, increases access speed, and reduces the load on central servers.
Benefits:
Example: using IoT devices to process data directly at the point of collection, for example, on sensors for industrial monitoring.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with cloud technologies allows companies to implement advanced analytical capabilities, machine learning, natural language processing, and other intelligent services without the need to invest in complex computing systems.
Benefits:
Example: Google Cloud AI, Amazon SageMaker, Microsoft Azure AI.
The growing focus on sustainability and environmental responsibility has led to the development of green cloud technologies. Cloud service providers are increasingly implementing strategies to reduce energy consumption and use renewable energy sources to power data centers. This helps to reduce the carbon footprint and make cloud computing more environmentally friendly.
Benefits:
Example: Microsoft has announced that its data centers have become carbon neutral and use 100% renewable energy.
The future of cloud computing looks very promising thanks to innovative approaches such as serverless computing, edge computing, artificial intelligence integration, and the development of green clouds. These trends are changing the way businesses store, process data and ensure system reliability, allowing them to operate faster, more efficiently and more environmentally friendly.
Cloud technologies are not only an innovation, but also a necessity for modern businesses that want to be efficient and competitive. They provide cost reduction, flexibility, security, and help to implement the latest technologies in work processes. The development of cloud solutions will only accelerate in the future.
Response










Ask us and our managers will contact you as soon as possible.